 Code
Code
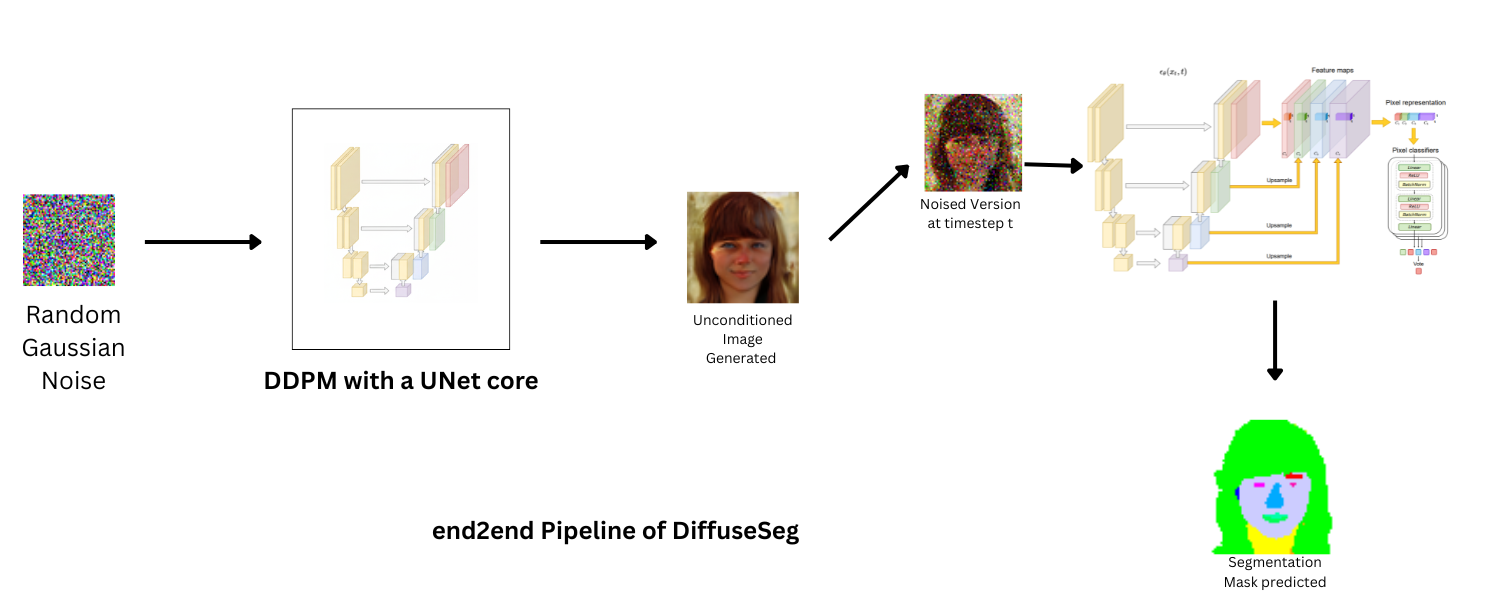
DiffuseSeg demonstrates how a single, unconditionally trained Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM) can serve as a powerful backbone for both high fidelity synthetic image generation and label-efficient semantic segmentation.

The core idea is to repurpose the rich, multi-scale features learned by the U-Net decoder of a DDPM. By extracting these features, we can train a lightweight, pixel level segmentation head with very few labeled examples, effectively turning the generative model into a labeled data factory.
This project was inspired by the following paper.
The project is implemented in two main stages:

With the DDPM U-Net frozen, we use it as a feature extractor.
This approach allows the model to generate a segmentation mask for any image—real or synthetically generated by the DDPM.
The segmentation head achieves strong performance on the CelebA-HQ validation set, demonstrating the quality of the features extracted from the trained DDPM.
Here are some end-to-end results, showing a synthetic image generated by the DDPM and the corresponding segmentation map produced by the MLP head.
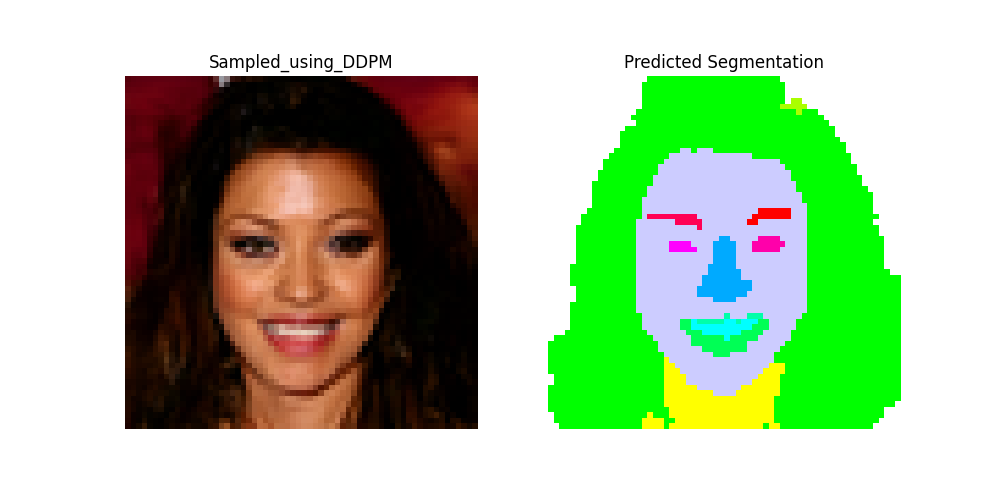
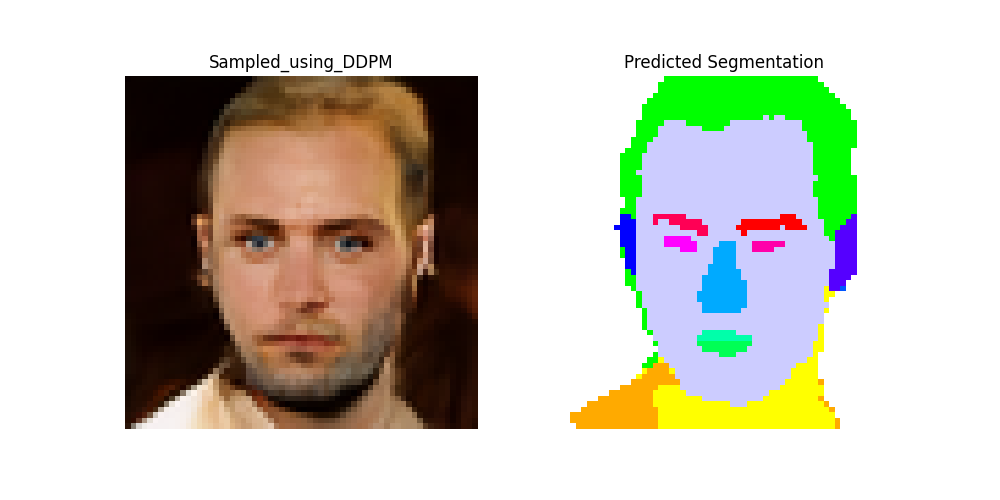


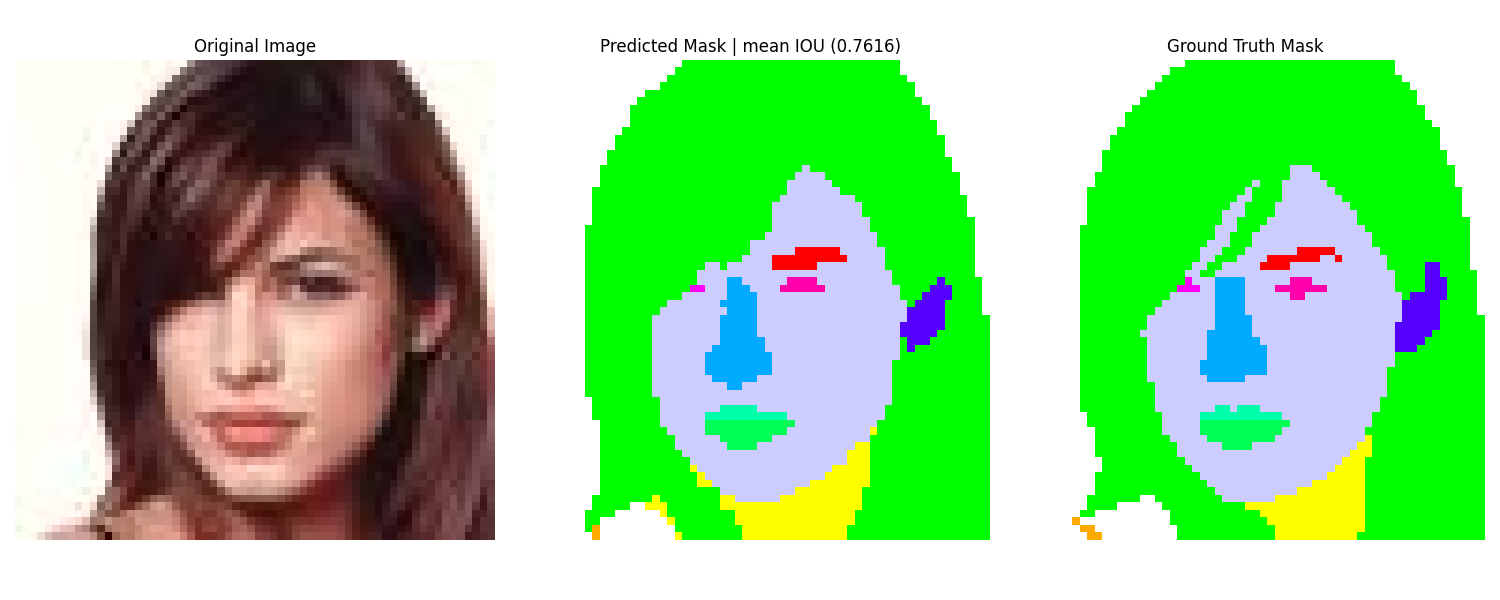
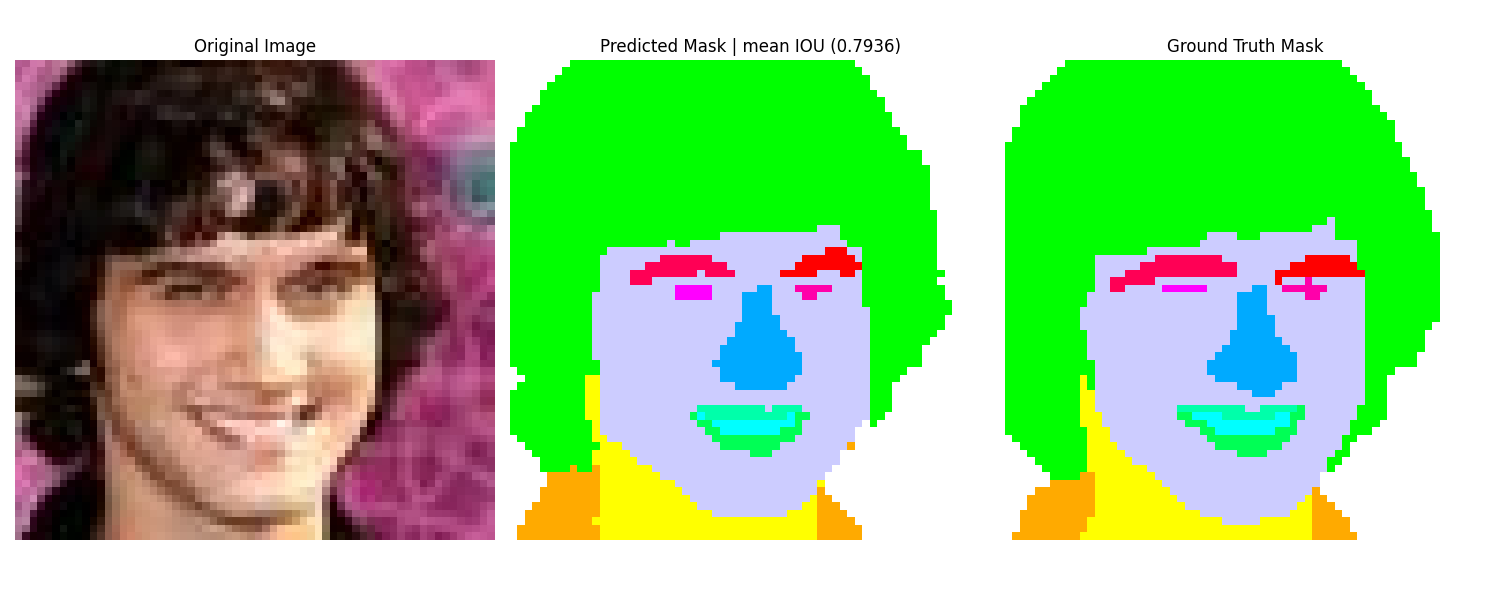
Here are some validation results, showing a image, its GT Mask from the CelebA-HQ Dataset accompanied by the corresponding segmentation map produced by DiffuseSeg.


git clone https://github.com/your-username/DiffuseSeg.git
cd DiffuseSegconda create -n diffuseg_env python=3.9
conda activate diffuseg_env
pip install -r requirements.txtTo train the diffusion model from scratch, use the DDPM-train.py script. Make sure your dataset path and training parameters are correctly set in utils/config.yaml. Also make dataset specific changes (im_size, im_channels) in the config file, while also noting that architectural changes (in terms of num of down/mid/up blocks ) can be made within config file.
python utils/DDPM-train.pypython utils/Feature_extractor.pypython utils/train_MLPs.pyDDPM_inference.py, and adjust inference params in config file.
python utils/DDPM_inference.pyDDPM-seg_inference.py, which returns predicted masks along with mIOU (mean IOU over all semantic parts) if GT Masks are provided.
python utils/DDPM-seg_inference.pyDiffuseSeg_e2e.py.
python utils/DiffuseSeg_e2e.pyFind below the original paper that inspired this approach:
@inproceedings{baranchuk2022label,
title={Label-Efficient Semantic Segmentation with Diffusion Models},
author={Dmitry Baranchuk and Ivan Rubachev and Andrey Voynov and Valentin Khrulkov and Artem Babenko},
booktitle={International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2022}
}